What Is Taurine?
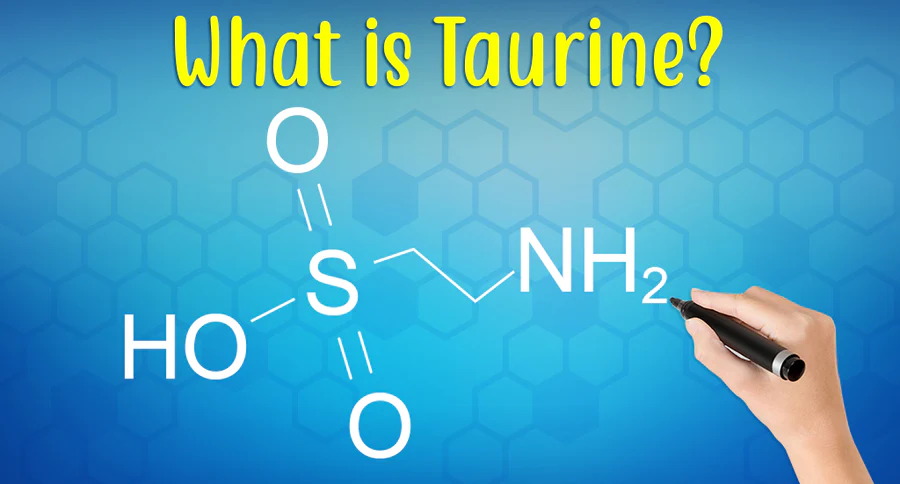
So what is taurine? Taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid, is a type of amino acid that is found in the body and is considered the most abundant amino acid in the heart, retina, skeletal muscle, brain and immune cells.
The word “taurine” stems from the Latin word taurus, which means bull or ox, because it was first isolated from ox bile in 1827 by German scientists Friedrich Tiedemann and Leopold Gmelin.
However, contrary to popular belief, there’s no association between taurine and bull sperm. Like the ingredient guarana, L-taurine is often added to energy drinks for those looking to take advantage of the potential taurine benefits. It’s also widely available in supplement form.
How Does Taurine Function in the Body?
Taurine is commonly referred to as a conditionally essential amino acid, meaning the body can produce it naturally, except in certain instances, like during illness and stress.
Taurine is synthsized from the antioxidant methionine and the amino acid cysteine in the presence of vitamin B6.
It plays an important role in various functions of the body, including maintaining electrolyte balance, formation of bile salts and fat digestion, and the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain.
It is also considered important to immune health due to its antioxidant properties. It’s also often used to enhance stamina in sports nutrition.
Because the body makes taurine, deficiency is rare. However, aging and different health conditions can reduce our body’s ability to make taurine.
Benefits
1)May boost exercise performance. Because of its ability to enhance muscle contraction and delay muscle fatigue, taurine may benefit athletic performance.
What’s more, taurine may increase fat burning during exercise to better fuel your performance.
2)May improve heart health.Taurine supplements have been shown to regulate blood pressure and improve heart function and blood fat levels in people with heart conditions such as heart failure. At high levels, it may even protect against heart disease.
Research suggests a link between higher taurine levels and reduced cholesterol, lower blood pressure levels, and significantly lower rates of death from heart disease
Taurine may help reduce high blood pressure by decreasing the resistance of blood flow in your blood vessel walls and by improving the efficiency of skeletal and heart muscle contractions.
3)Other health benefits.Other potential benefits of taking taurine supplements include
- May benefit eye health. Taurine’s antioxidant effects may help combat the oxidative stressassociated with retinal degenerative diseases such as age-related macular degeneration.
- May benefit hearing. Taurine may prevent the hair cells within the ear from becoming damaged, which is a key contributor to hearing loss.
- May offer neuroprotective effects. The anti-inflammatory effects of taurine may reduce inflammation within the brain and combat neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease.
- May support liver health. Taurine may have protective effects against chronic and acute liver injury.
How to supplement
The most common dosage range for taurine is 500–3,000 mg per day
However, keep in mind that an EFSA report from 2012 suggests that up to 6,000 daily is safe, demonstrating its strong safety profile.
While some studies may use a higher dose for short periods, sticking to 3,000 mg per day will help you maximize the benefits while staying within a safe range.
The easiest and most cost-effective way to reach this dosage is through powder or capsule supplements. Most capsule supplements contain 500–1,000 mg per serving, while powdered taurine can have 1,000–2,000 mg per serving.